Collection의 특징
- 제네릭(Generic) 이라는 기법으로 구현
예) class Person <T> {
public T name ;
}
Person<String>person = new Person <String>;
- 컬렉션의 요소는 객체들만 저장가능
* 기본 자료형(primitive type)의 데이터는 요소로 불가능
* 기본 타입의 값을 추가한 경우 자동 박싱(Auto Boxing)에 의해 Wrapper클래스로 변환되어 객체 형태로 저장
Collection > List > ArrayList
1. ArrayList
- 가장 보편적으로 많이 사용하는 컬렉션 클래스로 객체를 저장
- 크기가 고정이 아닌 가변의 길이
- 원하는 위치의 추가나 삭제가 쉬움
- ArrayList<E> //import java. util. ArrayList 생성// 사용하기 쉽게 library와 같음
// ArrayList 객체를 담을 수 있는 레퍼런스 변수 선언
ArrayList<String> list ;
// 객체 생성
new ArrayList<String>();
// 변수에 담기
list = new ArrayList<String>();
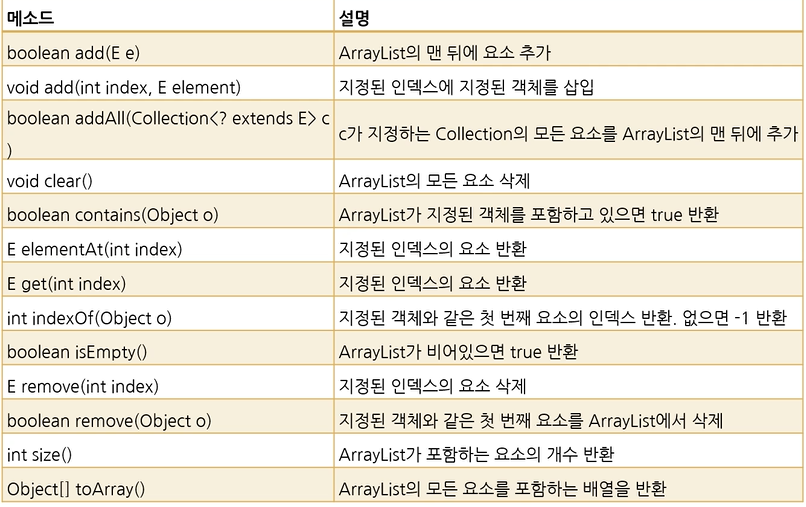
1) ArrayList<E>클래스의 주요 메소드
//요소의 개수 확인
System.out.println(list.size()); // 0출력
//요소 삽입
list.add("홍길동");
System.out.println(list.size()); // 1출력
list.add("동동일");
System.out.println(list.size()); // 2출력
// 요소 중간 삽입
list. add(1,"동동이");
System.out.println(list.size()); // 3출력
//요소 찾기
list.get(1);
System.out.println(list.get(2)); //동동일
//요소 부분 삭제
list.remove(1); // 첫번째 내용을 삭제
System.out.println(list.size()); //2 출력
System.out.println(list.get(1)); //동동일 출력
list.remove("동동이");
System.out.println(list.size()); // 2출력
System.out.println(list.get(0)); // 홍길동 출력
//요소 수정
list.set(0,"박나래"); //0번째를 박나래로 바꾸고 싶다.
System.out.println(list.get(0)); //박나래 출력
//요소 모두 삭제
list. clear();
System.out.println(list.size()); // 0 출력
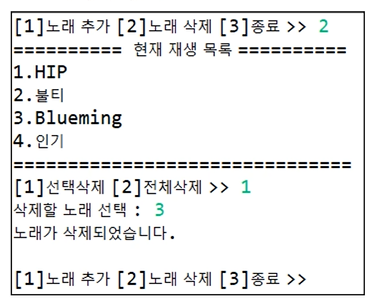
[예제]
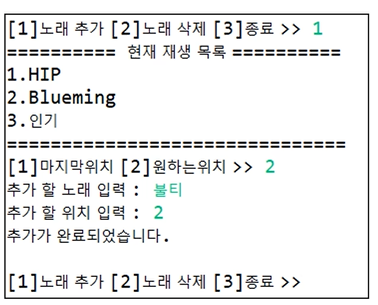
'[1]노래 추가' 선택시 list에 노래가 없을 경우 "재생목록이 없습니다. " 문장 출력/
노래가 있을 경우, 목록을 출력


ArrayList<String> musicList = new ArrayList<String>();
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in) ;
//노래 추가하기
musicList.add("HIP");
musicList.add("Blueming");
System.out.println("[1]노래추가 [2]노래삭제 [3]종료 >>");
int select = sc. nextInt();
while(true){
if (select==3) {
System.out.println("프로그램이 종료되었습니다.");
break;
} else if(select==1) {
System.out.println("======현재 재생 목록=====");
if(musicList.size()==0) { // 노래가 없을 경우
System.out.println("재생 목록이 없습니다.");
}else { // 노래가 있을 경우
for(int i =0; i<musicList.size(); i++) { //노래 개수 만큼
System.out.println(i+1+"."+musicList.get(i)); //노래 이름 출력
}
}
System.out.println("=====================");
}
}
System.out.println("=====================");
if(musicList.size()>0){
System.out.println("[1]선택삭제 [2] 전체삭제>.");
int removeSelect = sc. nextInt();
if(removeSelect==1) {
System.out.println("삭제할 노래 선택: ");
int index = sc. nextInt();
musicList.remove(index-1);
System.out.println("노래가 삭제되었습니다.");
}else if (removeSelect==2) {
musicList.clear();
System.out.println("전체 list가 삭제되었습니다.");
}
}
출처: 스마트인재개발원
'DATA 분석 교육 과정 (2024.02~08) > JAVA' 카테고리의 다른 글
| JAVA_상속 (0) | 2024.03.18 |
|---|---|
| JAVA_Music Playlist 만들기 (0) | 2024.03.18 |
| JAVA_정렬(Bubble-Sort, Selection-Sort / Sequential search, Binary search) (0) | 2024.03.17 |
| JAVA_배열, for-each, 이차배열 (0) | 2024.03.17 |
| JAVA_조건문(단순, if-else, 다중, switch) (0) | 2024.03.06 |


